Great Health Great Fitness
Conquer Cholesterol: Unlock Your Healthiest, Happiest Heart
Cholesterol plays a vital role in maintaining the proper functioning of our body. It is a type of lipid or fat found in every cell, necessary for producing certain hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids that help digest fat. However, when cholesterol levels in the blood become too high, it can lead to serious cardiovascular problems, such as heart disease and stroke.
Managing cholesterol is critical for ensuring long-term heart health. With the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases worldwide, the search for effective methods to lower cholesterol levels has grown significantly. The good news is that lowering cholesterol is often achievable with lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and sometimes, medications. This blog will explore the importance of cholesterol management, the different types of cholesterol, and practical methods to lower cholesterol effectively.
Understanding Cholesterol
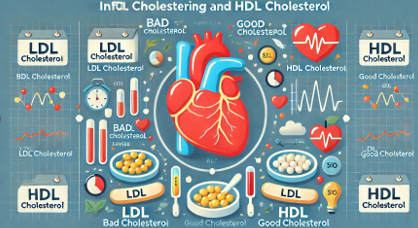
Cholesterol is carried through the bloodstream by two types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). It is crucial to understand the difference between these two to manage cholesterol levels effectively.
LDL Cholesterol (Bad Cholesterol)
LDL is the type of cholesterol that can build up on the walls of arteries, forming plaque and narrowing the arteries. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Therefore, it is important to keep LDL levels low.
HDL Cholesterol (Good Cholesterol)
HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from the blood and carries it to the liver, where it is either processed or excreted. High levels of HDL are beneficial as they protect against the harmful effects of LDL cholesterol.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are another type of fat in the blood. High triglyceride levels, especially when paired with low HDL or high LDL cholesterol, increase the risk of heart disease.
The key to heart health is balancing these lipid levels. Ideally, you want to lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol.
Why Cholesterol Management Matters
Excessive cholesterol in the blood can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this can lead to atherosclerotic heart disease, which significantly increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, making it imperative to manage cholesterol effectively.
The Silent Nature of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol often doesn’t show symptoms, making it a “silent” condition. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is crucial, especially for individuals with a family history of heart disease, those who are overweight or obese, or those who lead sedentary lifestyles. Cholesterol management can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases
The burden of cardiovascular diseases continues to grow globally. According to recent statistics, over 17 million people die from cardiovascular diseases each year. High cholesterol is a major risk factor in many of these cases, highlighting the need for proactive measures. Governments and healthcare organizations worldwide are focusing on raising awareness about cholesterol management to reduce these alarming figures.
Cholesterol and Your Age
Age is a significant factor in cholesterol levels. As we age, our body’s metabolism slows down, making it harder to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. For individuals over 40, regular cholesterol checks and proactive measures become even more critical. Early prevention strategies in younger individuals can also have long-term benefits, reducing risks later in life.
Methods to Lower Cholesterol Levels
While cholesterol management often requires a multi-faceted approach, there are several effective strategies for lowering cholesterol levels. These include adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and considering medication when necessary.
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in cholesterol management. Certain foods can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol, while others can have the opposite effect. Here are dietary tips to improve cholesterol levels:

1. Increase Fiber Intake
Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, barley, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables, binds to cholesterol in the digestive system and helps remove it from the body. A high-fiber diet can lower LDL cholesterol levels.
1.1. Practical Tips to Add More Fiber
- Start your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fruits like berries or bananas.
- Include legumes such as lentils or chickpeas in your soups and salads.
- Snack on raw vegetables like carrots, celery, or a handful of almonds.
- Choose whole-grain bread, rice, and pasta instead of their refined counterparts.
2. Choose Healthy Fats
Not all fats are created equal. Replace saturated fats (found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods) with unsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. These healthy fats can help increase HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol.
2.1 Debunking Myths About Fats
It is essential to differentiate between good fats and bad fats. While fats are often demonized, the body requires healthy fats for various functions, including hormone production and cell repair. By understanding which fats to prioritize, you can make more informed dietary choices.
3. Eat More Plant-Based Foods
Plant-based foods are naturally cholesterol-free and rich in nutrients that support heart health. Include a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes in your diet.
3.1. Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Reduces LDL cholesterol levels.
- Lowers blood pressure and inflammation.
- Provides antioxidants that protect against oxidative stress.
4. Limit Trans Fats
Trans fats are artificially created fats found in processed and packaged foods, such as baked goods, margarine, and fried foods. Trans fats increase LDL cholesterol levels and lower HDL cholesterol, so it’s important to avoid them.
4.1. How to Identify Trans Fats
- Check food labels for “partially hydrogenated oils.”
- Opt for fresh or minimally processed foods.
- Avoid fast foods and deep-fried items.
5. Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and flaxseeds, can help lower triglyceride levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week.
5.1. Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
For vegetarians or vegans, sources like chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds provide a good alternative.
6. Reduce Added Sugar
High consumption of added sugars, especially from sugary drinks and processed foods, has been linked to higher triglyceride levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Reducing sugar intake can contribute to better cholesterol management.
6.1. Practical Sugar Reduction Tips
- Substitute sugary drinks with water or herbal teas.
- Use natural sweeteners like honey or stevia sparingly.
- Limit dessert intake to special occasions rather than daily consumption.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is one of the most effective ways to raise HDL cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol. Regular exercise helps improve overall cardiovascular health and aids in weight management, which can further contribute to healthy cholesterol levels.

1. Aerobic Exercise
Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming is excellent for improving heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise.
1.1. Expanding Aerobic Options
- Explore group fitness classes like Zumba or dance workouts.
- Incorporate interval training for enhanced calorie burn and cardiovascular benefits.
2. Strength Training
Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help build muscle mass and improve cholesterol levels. Aim for at least two strength training sessions per week.
2.1. Home-Friendly Strength Options
- Use resistance bands or dumbbells.
- Practice bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, and planks.
3. Lifestyle Activities
In addition to formal exercise, try to incorporate more physical activity into your daily routine. Take the stairs instead of the elevator, go for short walks during breaks, and consider walking or biking instead of driving for short trips.
3.1. Tips to Stay Consistent
- Find a workout buddy for accountability.
- Set realistic and achievable fitness goals.
- Track your progress using fitness apps or journals.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can raise LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels while lowering HDL cholesterol. Losing weight can help improve these lipid levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
1. Portion Control
Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and bowls to help manage your portions.
1.1. Portion Control Techniques
- Measure servings with a kitchen scale or measuring cups.
- Avoid eating directly from packages to prevent overeating.
2. Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
Fill your plate with a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. These foods are lower in calories but rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
2.1. Set Realistic Goals
Aim for a gradual weight loss of 1 to 2 pounds per week. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of your total body weight can have significant benefits for cholesterol levels.
3. Overcoming Plateaus
Weight loss plateaus are common. When progress stalls, reassess your diet and exercise routine, and consider increasing the intensity or duration of your workouts.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption

1. Quit Smoking
Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol levels and damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Quitting smoking improves your HDL cholesterol levels and helps your heart and blood vessels heal.
1.1. Steps to Quit Smoking
- Seek support groups or counseling.
- Use nicotine replacement therapies if necessary.
- Identify and avoid triggers.
2. Limit Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise triglyceride levels and increase the risk of heart disease. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation—up to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
2.1. Choosing Heart-Healthy Options
If you choose to drink, red wine in moderation is considered heart-healthy due to its antioxidant properties. However, it’s essential to prioritize overall moderation.
Consider Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to achieve optimal cholesterol levels. If your cholesterol levels remain high despite dietary and lifestyle modifications, your doctor may recommend medications to help lower cholesterol. Some common cholesterol-lowering medications include:

1. Statins
Statins are the most commonly prescribed medication for lowering LDL cholesterol. They work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver that produces cholesterol.
2. Bile Acid Sequestrants
These medications help reduce LDL cholesterol by binding to bile acids in the digestive system, which forces the liver to use cholesterol to make more bile.
3. PCSK9 Inhibitors
These injectable medications help lower LDL cholesterol by blocking a protein that interferes with the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood.
4. Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors
These medications work by preventing the absorption of cholesterol from the food you eat.
5. Fibrates
Fibrates help lower triglycerides and can increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
If you’re on medication, regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial to monitor progress and adjust dosages if necessary.
The Psychological Connection to Cholesterol Management
Stress and mental health play a crucial role in cholesterol management. Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy behaviors such as overeating, poor dietary choices, and lack of exercise, all of which can elevate cholesterol levels. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation, can help maintain a balanced lifestyle and support heart health.

Strategies for Stress Reduction
- Practice deep breathing exercises daily.
- Engage in hobbies or activities that bring joy.
- Maintain a strong social support system.
Mental Health and Nutrition
- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids to support brain health.
- Stay hydrated and consume a balanced diet to maintain energy levels and reduce stress-induced cravings.
Conclusion
Cholesterol management is essential for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke. By adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, you can significantly improve your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. In some cases, medication may be necessary, but lifestyle changes should always be the first line of defense.
Regular monitoring of your cholesterol levels is key to staying on top of your heart health. If you have concerns about your cholesterol levels, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing your cholesterol and reducing your risk of heart disease. With the right approach, you can lower cholesterol, improve heart health, and live a longer, healthier life.
We’d love to hear from you! What steps are you taking to manage your cholesterol levels?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below – let’s start a conversation on how we can all live healthier, heart-strong lives!
If you found this information helpful, don’t forget to share this blog with your friends and family – because heart health is something we all need to prioritize!
For more tips on heart-healthy living, be sure to explore our products designed to support cholesterol management and overall well-being. Whether it’s dietary supplements, heart-healthy foods, or fitness guides, we have everything you need to take control of your cardiovascular health.
Stay heart-healthy, stay strong!
