Great Health Great Fitness
“The Complex Relationship Between Sugar and Weight Gain: A Comprehensive Analysis”
In this excerpt, we navigate through the multifaceted dynamics of how sugar affects our bodies, exploring both the physiological and behavioral aspects. From the impact of different types of sugars on metabolism to the role of sugary foods in calorie intake, we unravel the complexities underlying the link between sugar and weight gain. Through this comprehensive analysis, we aim to provide insights that empower individuals to make informed choices about their dietary habits and overall health.
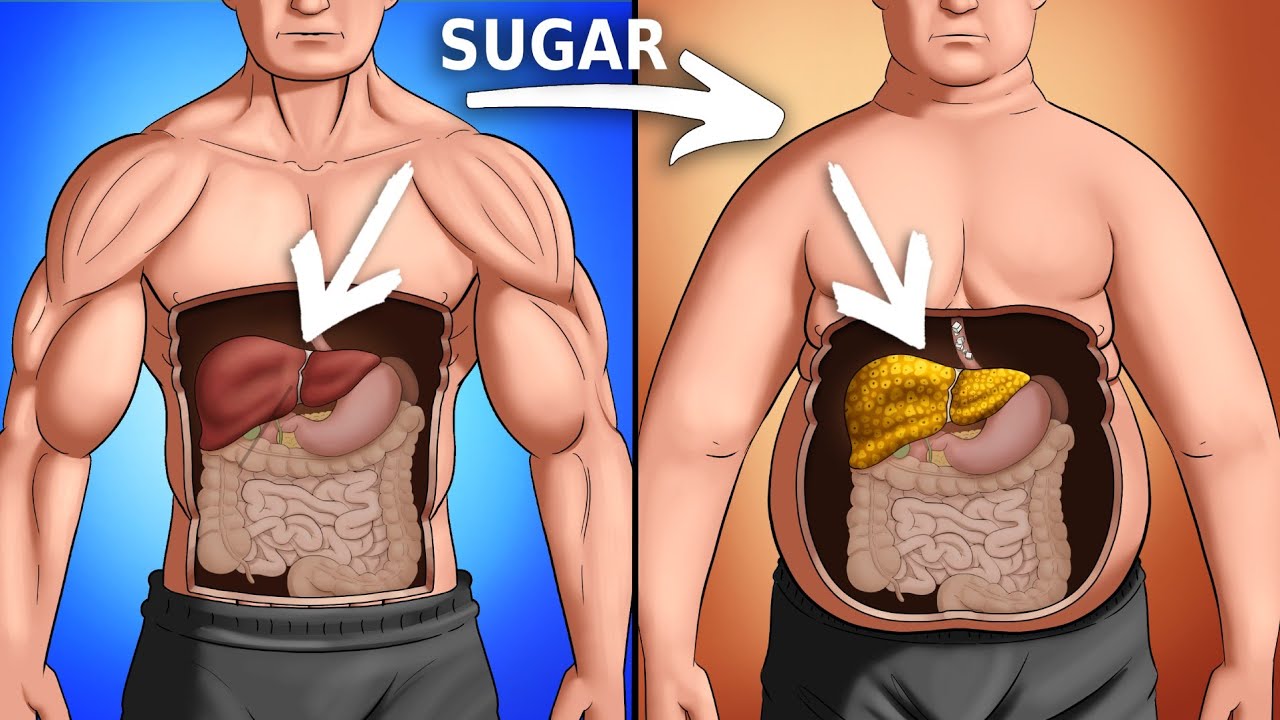

Introduction
The question of whether sugar makes you fat is one that has intrigued and concerned individuals for years. In the context of a world grappling with rising obesity rates and lifestyle-related health issues, understanding the intricate relationship between sugar consumption and weight gain is crucial. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into various aspects of this relationship, sweet, weight. exploring the physiological mechanisms, different types of sugars, and the broader context of overall diet and lifestyle.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324854#weight-gain
- Physiological Mechanisms:
- Caloric Balance: As previously discussed, weight gain occurs when there is a caloric surplus, regardless of the nutrient source. Consuming more calories than the body expends leads to the storage of excess energy as fat.
- Insulin Response: High sweet intake can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, triggering the release of insulin. Chronically elevated insulin levels may promote fat storage and interfere with the body’s ability to efficiently use energy, potentially contributing to weight gain.
- Satiety: Whole foods rich in natural sugars, such as fruits, tend to be more satiating due to their fiber content and nutrient density. In contrast, foods and beverages high in added sugars may lack satiety, leading to overconsumption and potential weight gain.
- Metabolic Effects: Excessive sweet consumption, particularly from sources high in added sugars, has been associated with adverse metabolic effects, including insulin resistance, inflammation, and dyslipidemia, which can contribute to weight gain and metabolic disorders.
- Types of Sugars:
- Naturally Occurring Sugars: Found in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, naturally occurring sweets are accompanied by beneficial nutrients and fiber.
- Added Sugars: Added sweets are incorporated into processed foods and beverages during manufacturing and provide empty calories without significant nutritional benefits.
- Broader Context:
- Dietary Patterns: Weight management involves considering the overall dietary pattern and caloric intake from all sources. A balanced diet rich in whole, minimally processed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, supports weight management and overall health.
- Lifestyle Factors: Beyond diet, factors such as physical activity levels, sleep quality, stress management, and overall lifestyle choices play crucial roles in weight management and metabolic health.
- Public Health Implications: Understanding the relationship between sugar consumption and weight gain is essential for addressing the global obesity epidemic and related health issues. Public health interventions, education campaigns, and policy changes aimed at reducing sweet intake and promoting healthier dietary habits can have significant impacts on population health.
Caloric Balance and Weight Gain
At its core, weight gain is fundamentally tied to the principle of caloric balance—consuming more calories than the body expends. This holds true regardless of the nutrient source. When an individual consistently consumes excess calories, sweet, weight. the surplus is stored in the form of fat. While sugar itself is a type of carbohydrate and a source of calories, it is essential to recognize that the overall caloric intake from all sources contributes to weight management.
- Energy balance: When individuals consistently consume more calories than their bodies expend through metabolism and physical activity, the excess energy is stored as fat, leading to weight gain over time. This surplus energy can come from any macronutrient, whether it be carbohydrates, fats, or proteins.
- Caloric content of sugar: Sweet, like other carbohydrates, provides energy, containing about 4 calories per gram. While it’s true that excessive sweet consumption can contribute to weight gain, it’s important to recognize that this is primarily due to the additional calories consumed rather than any unique properties of sugar itself.
- Context of overall diet: Weight management involves considering the overall dietary pattern and caloric intake from all sources, not just sweet. Consuming sugary foods and beverages in moderation as part of a balanced diet is unlikely to cause weight gain on its own. However, when sugar intake is excessive and contributes to a calorie surplus, it can certainly contribute to weight gain over time.
- Role of other nutrients: Focusing solely on sweet intake overlooks the broader context of dietary choices and their impact on weight management. Dietary patterns that are high in refined sweet often coincide with diets that are low in essential nutrients and fiber, which can influence satiety, metabolism, and overall health.
Types of Sugars
Not all sugars are created equal, and the source of sweet plays a significant role in its impact on the body. Naturally occurring sweet, such as those found in fruits, are accompanied by a host of other beneficial nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients contribute to overall health and can influence how the body processes and utilizes the sweet. On the other hand, added sugars, prevalent in many processed foods and sugary beverages, provide empty calories without the nutritional benefits found in whole foods.
- Nutrient density: Fruits, for example, not only provide natural sweet like fructose but also contain fiber, vitamins (such as vitamin C), minerals (such as potassium), antioxidants, and phytochemicals. Fiber, in particular, slows down the absorption of sweet into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels and promoting feelings of fullness.
- Satiety and digestion: The presence of fiber and other nutrients in whole foods slows down the digestion and absorption of sweet, providing a steady release of energy and promoting satiety. This can help regulate appetite and prevent overeating, contributing to weight management.
- Micronutrient absorption: Nutrients found in whole foods can also enhance the absorption and utilization of sugars by the body. For example, vitamin C enhances the absorption of iron from plant-based sources, which can be beneficial for individuals consuming iron-rich foods like spinach or lentils along with fruits.
On the other hand, added ssweets, which are incorporated into processed foods and beverages during manufacturing, provide little to no nutritional value beyond calories. These empty calories can contribute to weight gain and various health issues without providing any essential nutrients or health benefits.
- Caloric density: Added sweets increase the caloric density of foods without adding significant nutritional value, making it easier to consume excess calories and contribute to weight gain.
- Blood sugar spikes: Foods and beverages high in added sugars can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by crashes, leading to fluctuations in energy levels and potential cravings for more sugary foods.
- Risk of chronic diseases: Excessive consumption of added sugars has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other metabolic disorders.
Therefore, when considering the impact of sugar on health and metabolism, it’s essential to focus on the source of sugar and prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods over processed foods high in added sugars. By choosing whole foods rich in naturally occurring sweet, individuals can support overall health, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote weight management more effectively.

Insulin and Metabolism
High sugar intake has been associated with increased insulin levels, which play a crucial role in metabolism. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sweet levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. However, chronically elevated insulin levels, sweet, weight. often a result of frequent and excessive sugar consumption, can have implications for metabolism. Increased insulin levels may promote fat storage and interfere with the body’s ability to efficiently use energy.
When sugar is consumed in excess or too frequently, it can lead to chronically elevated blood sugar levels, which in turn trigger the release of more insulin from the pancreas. Over time, this can lead to a condition known as insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. As a result, the pancreas produces even more insulin to compensate for this resistance, leading to further increases in insulin levels.
Satiety and Overeating
The satiety factor is an important consideration in the sweet-weight gain relationship. Whole foods, which include natural sugars, tend to be more satiating due to their fiber content and the presence of various nutrients. In contrast, sugary foods and drinks may lack the same level of satiety, potentially leading to overeating. The absence of fiber and essential nutrients in many sugary products can result in a less satisfying eating experience, Sugar, weight. contributing to an overall increase in calorie consumption.
Fiber, in particular, plays a significant role in promoting satiety. It slows down digestion, prolonging the feeling of fullness and reducing the urge to eat again shortly after a meal. Additionally, fiber-rich foods tend to have a lower energy density, meaning they provide fewer calories per gram, which can help with weight management.
On the other hand, many sugary foods and beverages, such as candies, sodas, and pastries, are often low in fiber and other essential nutrients. These products tend to be highly processed, which can strip away fiber and other beneficial components found in whole foods. As a result, consuming sugary items may lead to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels followed by a crash, leaving individuals feeling hungry again soon after consumption.
Furthermore, research suggests that liquid calories, such as those from sugary drinks, may be less satiating than calories from solid foods. This is because liquids are not as physically filling as solid foods, and the body may not compensate for liquid calories by reducing food intake later in the day, potentially leading to an overall increase in calorie consumption.
Balanced Diet and Lifestyle
While sugar’s role in weight gain is a relevant factor, it is essential to recognize that weight management involves a holistic approach. A balanced diet, rich in a variety of nutrients, combined with regular physical activity and overall lifestyle choices, is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Singularly attributing weight gain to one specific nutrient oversimplifies the complex interplay of factors influencing body weight.
A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients is fundamental to maintaining a healthy weight and supporting overall health. This means prioritizing whole, minimally processed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that support various bodily functions and help regulate appetite and metabolism.
In addition to diet, regular physical activity is critical for weight management. Exercise helps burn calories, build muscle mass, and improve metabolic health, all of which contribute to weight maintenance and overall well-being. Incorporating a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises into one’s routine can maximize health benefits and support weight management efforts.

Holistic Approach to Nutrition
A holistic approach to nutrition emphasizes moderation, balance, and an understanding of overall dietary patterns. Singling out sweet as the sole culprit neglects the broader context of an individual’s eating habits. The quality of the overall diet, the diversity of food choices, and portion control are integral components of a healthy lifestyle.
Moderation involves consuming all foods in appropriate amounts, including those that contain sugar, fats, and other nutrients. Rather than demonizing specific foods or ingredients, moderation encourages mindful eating and enjoyment of a wide range of foods. This can help prevent feelings of deprivation and promote a more sustainable approach to healthy eating.
Balance is another important aspect of a holistic approach to nutrition. This involves incorporating a variety of foods from different food groups to ensure that the body receives essential nutrients and maintains optimal function. A balanced diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while also allowing for occasional treats or indulgences.
Understanding overall dietary patterns is crucial for assessing the impact of sugar and other dietary components on health. A diet that is rich in whole, minimally processed foods is generally associated with better health outcomes compared to one that is high in processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats. By focusing on the quality of the overall diet, individuals can make more informed choices that support their health goals.
Individual Factors
It’s important to acknowledge that individual responses to sugar and its impact on weight can vary significantly. Factors such as metabolism, genetics, age, and overall health play crucial roles in determining how the body processes and stores calories. Tailoring dietary recommendations to individual needs and characteristics is a key aspect of effective nutrition counseling.
Genetics also contribute significantly to how individuals respond to sugar. Genetic factors can influence taste preferences, insulin sensitivity, and predispositions to conditions like obesity or diabetes. For example, some people may have a heightened sweet tooth due to genetic variations in taste receptors, while others may be more prone to insulin resistance, impacting how their bodies handle sugar intake.
Age is another critical factor to consider. Metabolic rates tend to decrease with age, making it easier to gain weight and more challenging to lose it. Additionally, hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can affect how the body processes and stores sugar and fat.
Overall health plays a crucial role in shaping individual responses to sugar. Conditions like diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and thyroid disorders can alter carbohydrate metabolism and impact weight management. Medications and lifestyle factors, such as physical activity levels and stress levels, also interact with sugar metabolism, further influencing individual outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between sugar and weight gain is nuanced and multifaceted. While excessive sweet consumption can contribute to an imbalance in caloric intake and potentially lead to weight gain, it is just one piece of the larger puzzle. Understanding the types of sugars, considering the impact on insulin and metabolism, and adopting a holistic approach to nutrition are essential for a comprehensive perspective on this issue. Rather than demonizing sugar outright, it is more productive to focus on cultivating a well-rounded and balanced approach to diet and lifestyle for long-term health and weight management. For personalized guidance, individuals should consult healthcare professionals or registered dietitians who can provide tailored advice based on specific needs and circumstances.
For More Information you can check our blogs The Dynamic Impact of Empowering Positive Mantras: 5 Crafting a Resilient Mindset for Lasting Transformation and Unleashing Positive Energy.

[…] In conclusion, deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective tool for reducing stress and promoting relaxation. By incorporating deep breathing into your daily routine, you can activate the body’s relaxation response, calm the mind, and alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety. Whether practiced as a standalone technique or combined with other relaxation strategies, such as meditation or progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing offers a convenient and accessible way to manage stress and enhance overall well-being. Remember to take regular breaks throughout the day to practice deep breathing and cultivate a greater sense of calm, balance, and resilience in your life. For more information you can check our blogs “The Complex Relationship Between Sugar and Weight Gain: A Comprehensive Analysis”. […]