Great Health Great Fitness
“Living with Diabetes: Empowering Lifestyle Strategies for Effective Management”
Living with diabetes requires a proactive approach to managing one's health and well-being. By incorporating empowering lifestyle strategies, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges of diabetes and achieve better health outcomes. From adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity to leveraging technology for monitoring blood sugar levels, there are various ways to take control of diabetes management. With dedication, education, and support, living well with diabetes is not just achievable but empowering.

Introduction
Living with Diabetes requires a proactive and holistic approach to manage the condition effectively. This comprehensive blog post explores lifestyle strategies that empower individuals with diabetes to lead fulfilling lives while maintaining optimal health. From dietary considerations to physical activity and emotional well-being, this guide aims to provide valuable insights for those navigating the challenges of diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes: A Holistic Perspective

Begin by offering a brief overview of diabetes types and the impact on the body. Discuss the importance of a holistic understanding of diabetes management, encompassing physical, dietary, and emotional aspects.
Managing effectively requires a holistic approach that addresses not only the physical aspects but also the dietary and emotional aspects of the condition. Physical activity plays a crucial role in diabetes management by improving insulin sensitivity, controlling blood sugar levels, and reducing the risk of complications. Regular exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves cardiovascular health, all of which are important considerations for individuals with diabetes.
In addition to physical activity, dietary choices play a significant role in management. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels, promote weight management, and reduce the risk of complications. Monitoring carbohydrate intake, paying attention to portion sizes, and limiting added sugars and refined carbohydrates are important dietary strategies for individuals with diabetes.
Emotional well-being is another crucial component of diabetes management. Living with a chronic condition can be challenging and may lead to feelings of stress, anxiety, or depression. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes to prioritize self-care, seek support from healthcare providers, family, and friends, and develop coping strategies to manage emotional stressors effectively. Engaging in relaxation techniques, practicing mindfulness, and participating in support groups or counseling can also help improve emotional well-being and overall quality of life.
Nutrition for Diabetes: Crafting a Balanced Diet

Explore the fundamental principles of a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes. Discuss the significance of carbohydrate counting, the glycemic index, and portion control. Provide practical tips for meal planning and maintaining nutritional balance.
A balanced diet is essential for individuals with sweet to manage blood sugar levels effectively and maintain overall health. Central to this approach is carbohydrate counting, a method that involves monitoring the amount of carbohydrates consumed in each meal and matching it with insulin doses or medication as needed. Understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods is also crucial, as it indicates how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Choosing low-GI foods, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent spikes.
Additionally, portion control plays a significant role in managing diabetes, as consuming appropriate serving sizes helps regulate calorie intake and blood sugar levels. Practical tips for meal planning include incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as lean proteins, healthy fats, and high-fiber carbohydrates, into each meal. This ensures balanced nutrition while helping to control blood sugar levels. Moreover, spreading carbohydrate intake evenly throughout the day and pairing carbohydrates with protein and fiber-rich foods can further aid in blood sugar management. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and working closely with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can help individuals with diabetes tailor their diet to meet their specific needs and achieve optimal health outcomes.
The Role of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management
Highlight the benefits of regular physical activity for individuals with diabetes. Discuss suitable exercise routines, the importance of incorporating both aerobic and strength training, and offer motivational tips for staying active.
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes, including improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of cardiovascular complications, weight management, increased energy levels, and enhanced overall well-being. Suitable exercise routines for individuals with diabetes should incorporate both aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing, and strength training activities, such as lifting weights or resistance band exercises. Aerobic exercises help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and improving glucose uptake by muscles. Strength training activities, on the other hand, help build muscle mass, which can further enhance insulin sensitivity and contribute to better blood sugar control.
Motivational tips for staying active with diabetes include setting realistic goals, finding activities that are enjoyable and sustainable, and incorporating exercise into daily routines. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activity over time to avoid injury and burnout. Tracking progress, celebrating achievements, and seeking support from friends, family, or a healthcare provider can also help maintain motivation and adherence to an exercise routine.
Additionally, focusing on the immediate benefits of exercise, such as improved mood, increased energy, and stress reduction, can provide further motivation to stay active. Remembering that every step counts and that consistency is key to long-term success can help individuals with diabetes stay motivated and committed to regular physical activity.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: Tools and Techniques
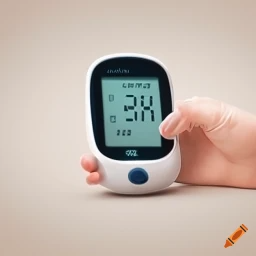
Discuss the importance of regular blood glucose monitoring in diabetes management. Explore the different tools available for monitoring, including traditional glucose meters and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems.
Traditionally, individuals with sweet have used glucose meters to measure their blood sugar levels. These handheld devices require a small blood sample obtained by pricking the fingertip with a lancet. The blood is then placed on a test strip inserted into the meter, which provides a digital readout of the blood glucose level within seconds. Glucose meters are portable, relatively inexpensive, and easy to use, making them a convenient option for regular monitoring.
In recent years, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have gained popularity among individuals with diabetes. CGM systems consist of a tiny sensor inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen, that continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor transmits this information wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone app, providing real-time data on blood sugar trends, patterns, and fluctuations throughout the day and night.
CGM systems offer the advantage of providing more comprehensive and detailed information about blood sugar levels, including trends and patterns that may not be captured by traditional glucose meters. This continuous monitoring can help individuals make more timely and proactive adjustments to their diabetes management regimen, such as adjusting medication dosages, modifying dietary choices, or altering physical activity levels.
Medication Adherence and Treatment Plans
Address the significance of adhering to prescribed medications and treatment plans. Provide insights into the various types of diabetes medications, their mechanisms, and how they complement lifestyle strategies.
Oral medications, such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, and SGLT2 inhibitors, work by different mechanisms to enhance insulin action, reduce glucose production, and improve insulin sensitivity. Injectable medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists offer additional options for blood sugar control in Type 2 diabetes. These medications complement lifestyle strategies, including healthy eating, regular exercise, and stress management, by optimizing blood sugar regulation and overall health. By adhering to prescribed medications and treatment plans, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition, minimize complications, and lead healthier lives.
Emotional Well-being and Stress Management
Recognize the emotional impact of living with diabetes and discuss strategies for managing stress. Explore the connection between mental health and diabetes, emphasizing the importance of mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and seeking support.
Managing stress is crucial for individuals with sweet to maintain overall well-being and effectively control their blood sugar levels. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, can help reduce stress and promote emotional balance. These techniques can be incorporated into daily routines to cultivate a sense of calm and resilience in the face of challenges.
In addition to mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and aromatherapy can help alleviate stress and promote relaxation. These techniques can be particularly beneficial during times of heightened stress or anxiety.
Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can also be helpful for managing the emotional impact of diabetes. Talking about feelings and concerns with trusted individuals can provide validation, reassurance, and practical advice for coping with the challenges of living with diabetes. Support groups or counseling can offer additional opportunities for sharing experiences, gaining insights, and learning coping strategies from others who are facing similar challenges.
Building a Support System: Family, Friends, and Healthcare Professionals
Discuss the role of a robust support system in diabetes management. Explore how involving family and friends, as well as maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals, can contribute to a positive and proactive approach.
Family and friends can offer practical assistance by helping with meal preparation, exercise routines, and medication reminders. They can also provide emotional support by listening, offering encouragement, and helping individuals cope with the challenges and frustrations of living . Additionally, involving loved ones in diabetes management can foster a sense of teamwork and shared responsibility, empowering individuals to take charge of their health and well-being.
Maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals is also essential for effective diabetes management. Healthcare providers play a critical role in guiding treatment decisions, monitoring progress, and addressing any concerns or challenges that may arise. By communicating openly and honestly with their healthcare team, individuals with diabetes can receive personalized guidance, support, and education to optimize their treatment plan and achieve their health goals.
Regular check-ups, screenings, and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring blood sugar levels, assessing overall health, and addressing any complications or concerns that may arise. Building a trusting and collaborative relationship with healthcare providers can help individuals feel supported and empowered to navigate the complexities of diabetes management effectively.
Navigating Social Situations and Challenges
Address the challenges individuals with diabetes may face in social settings. Provide practical tips for managing diabetes during special occasions, dining out, and navigating peer pressures.
During special occasions, such as holidays or celebrations, it’s essential for individuals with diabetes to plan ahead and anticipate potential challenges. This may involve monitoring blood sugar levels more frequently, adjusting insulin doses or medication schedules as needed, and being mindful of portion sizes and carbohydrate intake. Bringing along diabetes-friendly snacks or dishes to share can also ensure there are healthy options available.
When dining out, individuals with sweet can make informed choices by reviewing restaurant menus ahead of time, looking for options that are lower in carbohydrates and higher in fiber and protein. Asking for modifications, such as substituting starchy sides for vegetables or opting for grilled or baked dishes instead of fried, can help control blood sugar levels. Additionally, practicing portion control and sharing meals with others can prevent overeating and minimize blood sugar spikes.
Peer pressures related to food choices and alcohol consumption can present challenges for individuals with diabetes, especially in social settings where unhealthy foods and beverages are prevalent. It’s essential for individuals to assertively communicate their dietary preferences and health needs to friends and peers, while also advocating for themselves and their well-being. Setting boundaries around food and alcohol consumption, sticking to personal health goals, and finding alternative ways to socialize that don’t revolve around food or alcohol can help individuals with diabetes navigate peer pressures effectively.
Integrating Technology in Diabetes Management
Explore the role of technology in diabetes care. Discuss the benefits of smartphone apps, wearable devices, and other technological advancements in monitoring and managing diabetes.
Smartphone apps designed for management offer a wide range of features, including blood glucose tracking, carbohydrate counting, meal planning, medication reminders, and data analysis. These apps allow individuals to conveniently record and monitor their blood sugar levels, track food intake, and log physical activity, providing valuable insights into their overall health and well-being. Additionally, some apps offer personalized recommendations and coaching based on individual data, helping users make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
Wearable devices, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps, have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time data and automated delivery of insulin. CGMs continuously monitor blood sugar levels throughout the day and night, providing users with instant feedback and alerts for high or low blood sugar levels. Insulin pumps deliver precise doses of insulin based on CGM data, offering greater flexibility and control over insulin therapy.
Other technological advancements in diabetes care include smart insulin pens, which track insulin doses and provide reminders for injections, and telemedicine platforms, which allow individuals to consult with healthcare providers remotely for personalized guidance and support. These technologies empower individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition, improving adherence to treatment plans and overall health outcomes.
Future Innovations and Research in Diabetes Management
Highlight ongoing research and potential future innovations in diabetes management. Discuss emerging technologies, treatment modalities, and advancements that may shape the future of diabetes care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of living with diabetes is dynamic and multifaceted. By incorporating these lifestyle strategies, individuals can navigate the challenges, embrace a positive mindset, and lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition. Continuous collaboration with healthcare professionals, staying informed, and fostering a supportive network are integral components of a successful approach to management. The key is to empower individuals with diabetes to thrive and prioritize their overall well-being. For more information you can check our blogs The Future of Healthcare: AI, Robotics, and Digital Health Empowering Patient Care.
